Connectors are indispensable components for connecting wiring harnesses to other electrical equipment. The TPA and CPA of connectors are mainly used to fix the positions of terminals and connectors.
CPA, plastic case secondary locking mechanism, Connector Position Assurance. Its function is to ensure that the buckle of the primary locking mechanism will not be easily withdrawn after the plastic case and electrical interface are assembled in place. Due to its special functions, the CPA must ensure the operability and legibility of workers when designing. This requires that the CPA must be an independent mechanism on the plastic shell and must also have a special color mark.
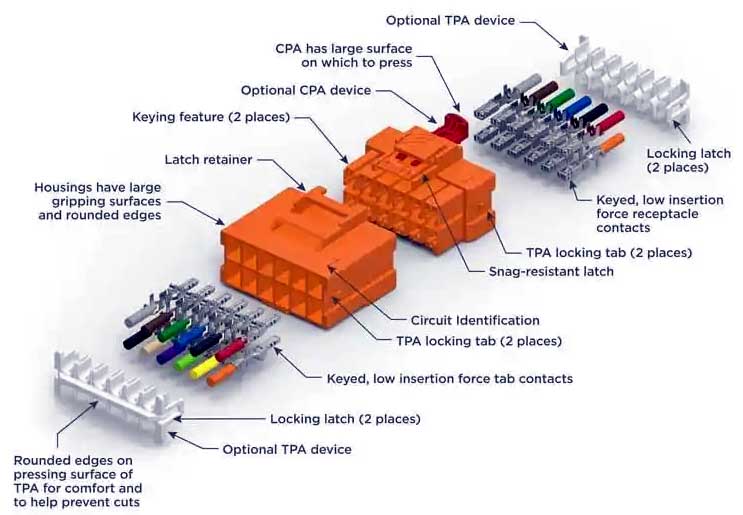
Standard 02-LV214 for CPA and TPA connectors
TPA, terminal secondary locking structure, Terminal Position Assurance. Not all terminals require secondary locking structures. The public requirement is that TPA should be used when the terminal width is less than 2.8mm (including 2.8). In order to ensure easy installation by workers in the wiring harness factory, the color of TPA must also be identifiable, and the TPA must have a clear feel during assembly. In order to ensure that the TPA will not automatically enter the locking position when the plastic case is transported to the wiring harness factory, an anti-locking mechanism is necessary on the TPA.
Among the performance of the connector, the connector’s own plug-in fixing mechanism and the reliability of the terminal fixing in the connector are also very important. If there is a problem with the connector’s own fixing mechanism or the reliability of the terminal fixing in the connector, it will seriously affect the contact reliability of the connector and bring more serious consequences. This article mainly continues the analysis of the standard to talk about the relevant content;
Connector Position Assurance (CPA)
Terminal Position Assurance (TPA)
Primary Lock Reinforcement (PLR)
Positive-locking contact
Friction-locking contact

KR2017 Wire-to-Board Connector TPA Lock Engaged – Contacts are properly positioned and cannot be removed
We may be most familiar with CPA and TPA. Simply put, one is to fix the connector position and the other is to fix the terminal position. Many times when the primary lock is more reliable (the structural lock of the connector itself), CPA can be cancelled and is not necessarily necessary. Many people think that this is a must, which is incorrect, unless it is required by some vibrating equipment installation surfaces. TPA is mainly used to fix the terminal position. Of course, the terminal can be fixed on the TPA slot and structurally fixed by TPA and the connector, or it can be used as a stop after the terminal is inserted into the connector (the terminal structure itself often has a primary lock and a secondary lock). The specific description is not expanded here;
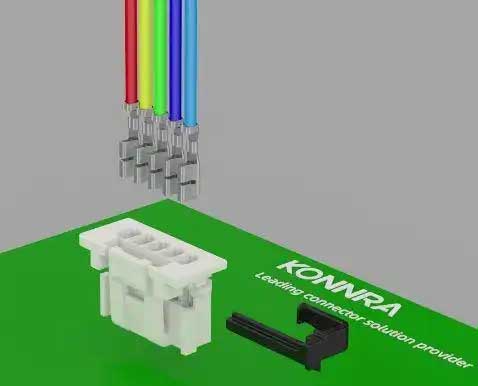
Terminal Position Assurance (TPA) – KR2017 Wire-to-Board Connector TPA Lock Disengaged – Contacts are not fully seated and can be removed freely
Interaction between contacts and contact housings
This test is mainly to verify the functions of the connector cavity and terminal lock. According to the standard requirements, 3 sets of connectors are prepared for test verification from the appearance, terminal positioning accuracy, primary lock function, and secondary lock function. It is necessary to meet the reliability of related functions after the drop test. The main lock needs to meet the tensile force of at least 10N, and the secondary lock needs to meet the driving force requirements in the table;
Operation and functional reliability of contact housings
This test is mainly to check the retention and driving force of the terminal housing. Two related forces are mainly investigated, one is the related driving force of the positioning device CPA, the force of accidental operation, atd. The other is the insertion and separation force of the connector, such as the connector insertion force must be ≤75N (Insertion/actuation force of fully equipped contact housings: ≤ 75 N). According to the requirements of different PIN numbers and different terminal locking methods, the corresponding housing retention force is also different. The larger the number of pins, the wider the pins (default insert type) and the greater the required holding force. Compared with the requirements of USCAR-2 or GMW319, the force requirement of LV214 in this area is still relatively small.
 English
English العربية
العربية Български
Български Čeština
Čeština Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Magyar
Magyar Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
